2-3 组织并行线程
2.3 组织并行线程
从前面的例子可以看出,如果使用了合适的网格和块大小来正确地组织线程,那么可以对内核性能产生很大的影响。在向量加法的例子中,为了实现最佳性能我们调整了块的大小,并基于块大小和向量数据大小计算出了网格大小。
现在通过一个矩阵加法的例子来进一步说明这一点。
2.3.1 使用块和线程建立矩阵索引
通常情况下,一个矩阵用行优先的方法在全局内存中进行线性存储(最简单)。图2-9所示的是一个8×6矩阵的小例子。
在一个矩阵加法核函数中,一个线程通常被分配一个数据元素来处理。首先要完成的任务是使用块和线程索引从全局内存中访问指定的数据。通常情况下,对一个二维示例来说,需要管理3种索引:
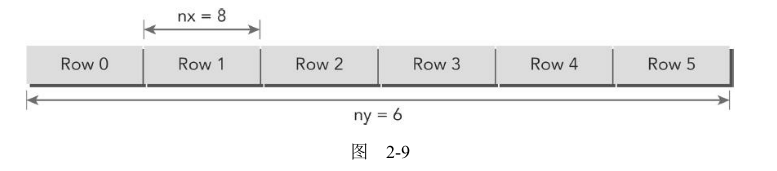
- 线程和块索引
- 矩阵中给定点的坐标
- 全局线性内存中的偏移量
图2-10说明了块和线程索引、矩阵坐标以及线性全局内存索引之间的对应关系。
内存的索引代码如下
1 | __global__ void printThreadIndex(int *A, const int nx, const int ny) |
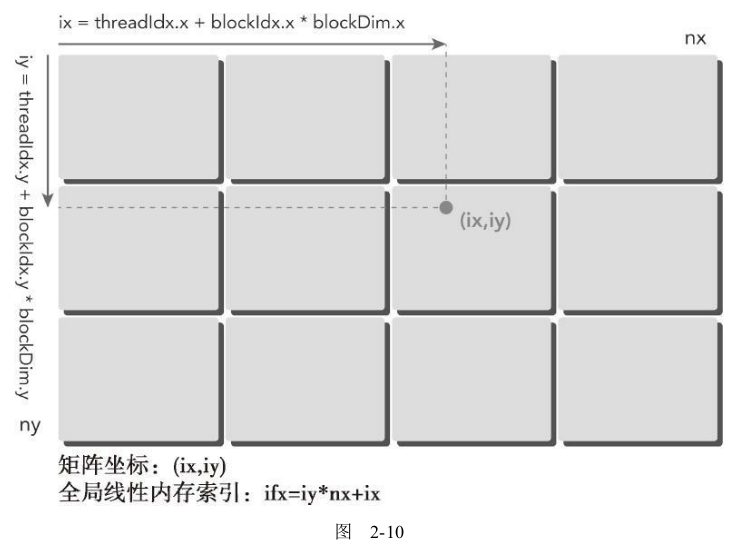
由于我们测试的是8*6的矩阵(内存的内容和内存索引设定相同,方便分析),
- nx=8 ny=6 也就是
8*6的矩阵 - block 设定为(4,2),也就是一个block在x方向上有4个线程,在y方向上有2个线程
- grid计算得出(2,1),也就是一个grid在x方向上有2个block,在y方向上有1个block
- 一个线程对应一个内存地址计算
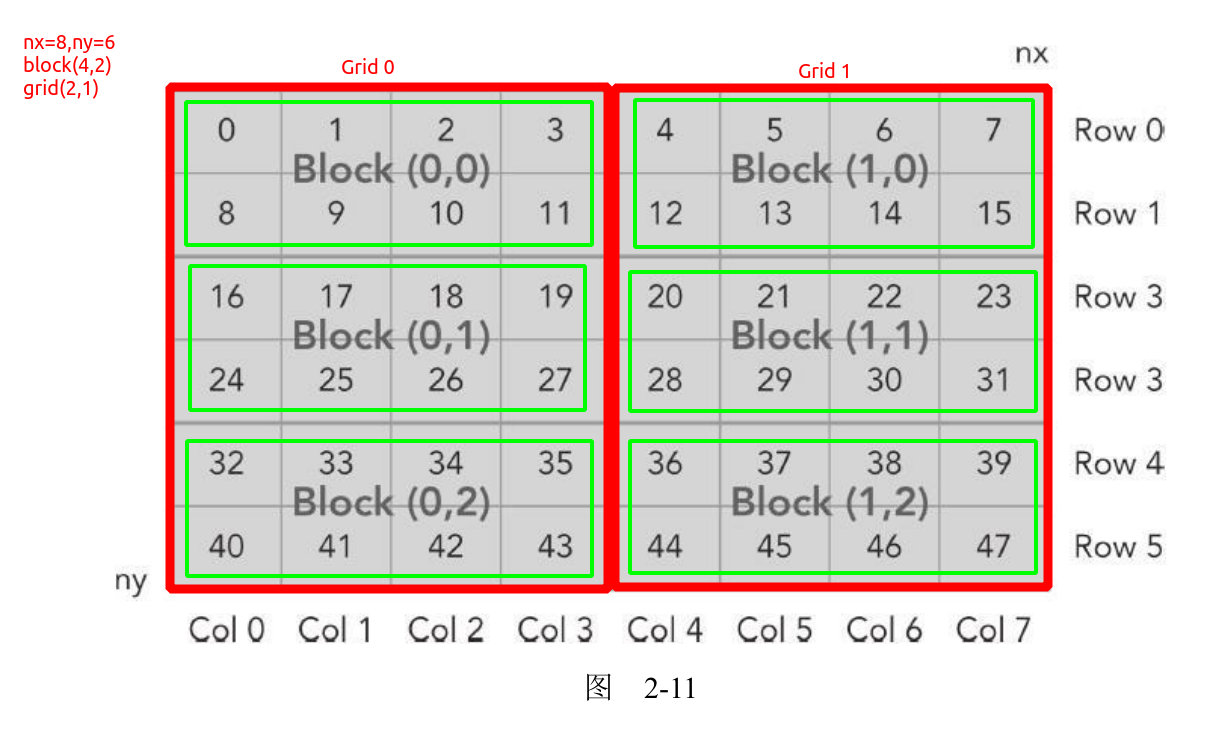
注意:下图中红色框是grid的索引(图中描述的不太合适,意思就是grid在x方向上有2个block索引,在y方向上有一个索引)。绿色框是block的索引(图中描述的不太合适,意思就是block在x方向上有4个thread索引,在y方向上有2个thread索引)。需要注意的是内存的排列,例如block(0,0)中线程对应的内存索引的是0,1,2,3和8,9,10,11,而不是0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7。下面会有程序的测试结果
下面的代码打印了对应的索引
1 | //chapter02/checkThreadIndex.cu |
结果如下:
1 | ./checkThreadIndex Starting... |
以第一个block(0,0)为例,可以看到内存索引的确是0,1,2,3,8,9,10,11
1 | thread_id (0,0) block_id (0,0) coordinate (0,0) global index 0 ival 0 |
2.3.2 使用二维网格和二维块对矩阵求和
有了上面一节的内存索引,就可以计算两个矩阵的和了。和上一节的kernel几乎一样,也是索引到内存,但是多了一步数组相加的代码如下:
1 | // grid 2D block 2D |
另外修改了矩阵和block的维度
1 | // set up data size of matrix |
程序完成代码如下:
1 | //sumMatrixOnGPU-2D-grid-2D-block.cu |
编译运行如下
1 | ./sumMatrixOnGPU-2D-grid-2D-block |
书中修改了bloc大小为(32,16)性能翻了一倍,但是我自己测试变化不大,但是有一个结论就是不同的block和grid配置会影响到核函数的性能。
2.3.3 使用一维网格和一维块对矩阵求和
前面两节都是二维网格二维块来计算二维的矩阵,比较好理解。
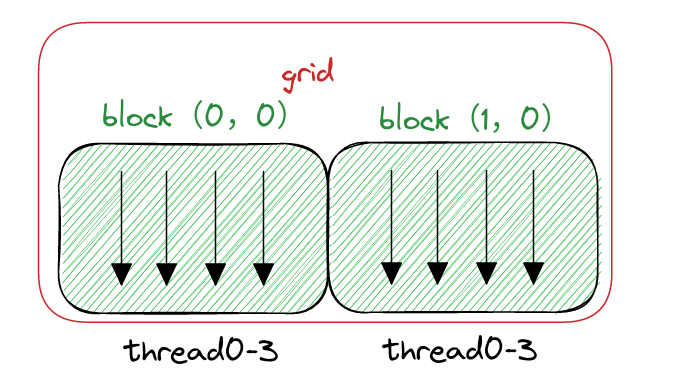
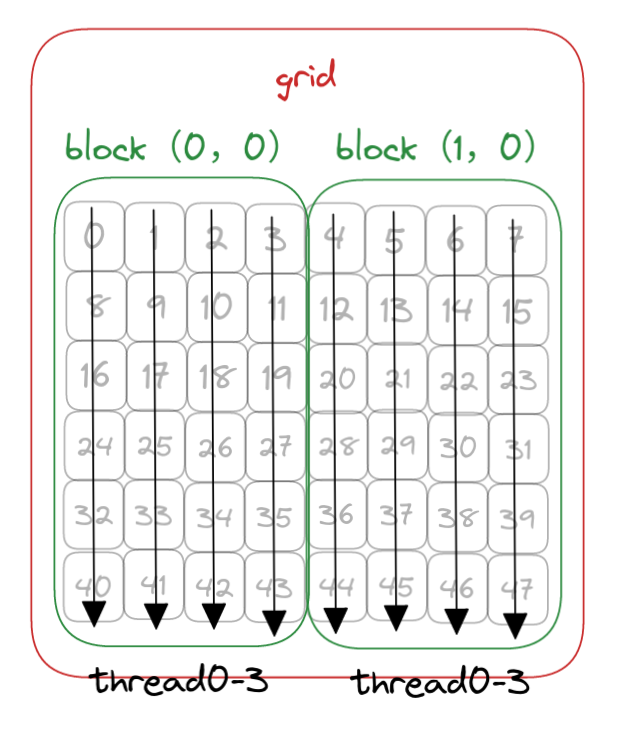
为了使用一维网格和一维块,你需要写一个新的核函数,其中每个线程处理ny个数据元素,如图2-13所示。

下图假如矩阵还是8*6
- nx=8 ny=6 也就是
8*6的矩阵 - block 设定为(4,1)
- grid计算得出(2,1)
- 与上面两节不同,一个线程需要计算6个内存的数据
- 下图中黑色的箭头代表一个线程,每个block有4个线程
- 灰色的数字是内存的内容,一个线程(箭头)处理6个数据,例如第一个线程处理的就是0,8,16,54,32,40共6个数据
- 绿色为一个block,红色为grid
对应的核函数代码为
1 | // grid 1D block 1D |
完整的代码修改了数据的维度和block的维度
1 | //chapter02/sumMatrixOnGPU-1D-grid-1D-block.cu |
运行结果如下
1 | ./sumMatrixOnGPU-1D-grid-1D-block |
2.3.4 使用二维网格和一维块对矩阵求和
这可以看作是含有一个二维块的二维网格的特殊情况,其中块的第二个维数是1。因此,从块和线程索引到矩阵坐标的映射就变成:
- 一个线程对应一个内存地址计算
核函数代码为
1 | // grid 2D block 1D |
完整代码如下:
1 |
|
运行结果如下
1 | ./sumMatrixOnGPU-2D-grid-1D-block |
对比上面两节的结果
1 | zmurder@zmurder:~/WorkSpace/zyd/note/cuda/CUDA C编程权威指南/CUDAC编程权威指南练习code/chapter02$ ./sumMatrixOnGPU-2D-grid-2D-block |
从矩阵加法的例子中可以看出:
- 改变执行配置对内核性能有影响
- 传统的核函数实现一般不能获得最佳性能
- 对于一个给定的核函数,尝试使用不同的网格和线程块大小可以获得更好的性能
在第3章,将会从硬件的角度学习产生这些问题的原因。