3-4 避免分支分化
3.4 避免分支分化
线程束中的条件执行可能引起线程束分化,这会导致内核性能变差。通过重新组织数据的获取模式,可以减少或避免线程束分化。在本节里,将会以并行归约为例,介绍避免分支分化的基本技术。
3.4.1 并行归约问题
假设要对一个有N个元素的整数数组求和。如何通过并行计算快速求和呢?鉴于加法的结合律和交换律,数组元素可以以任何顺序求和。所以可以用以下的方法执行并行加法运算:
- 将输入向量划分到更小的数据块中。
- 用一个线程计算一个数据块的部分和。
- 对每个数据块的部分和再求和得出最终结果。
成对的划分常见的方法有以下两种:
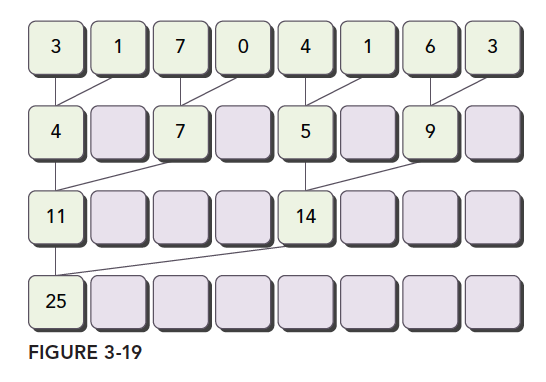
相邻配对:元素与他们相邻的元素配对
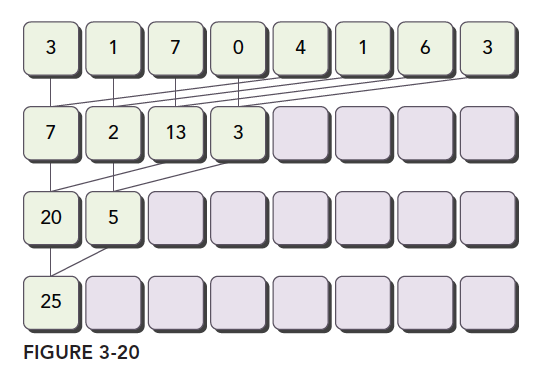
交错配对:元素与一定距离的元素配对
下面是CPU版本的交错配对的实现:
1 | // Recursive Implementation of Interleaved Pair Approach |
在向量中执行满足交换律和结合律的运算,被称为归约问题。并行归约问题是这种运算的并行执行
3.4.2 并行归约中的分化
图3-21所示的是相邻配对方法的内核实现流程(一个线程块内的运算)。每个线程将相邻的两个元素相加产生部分和。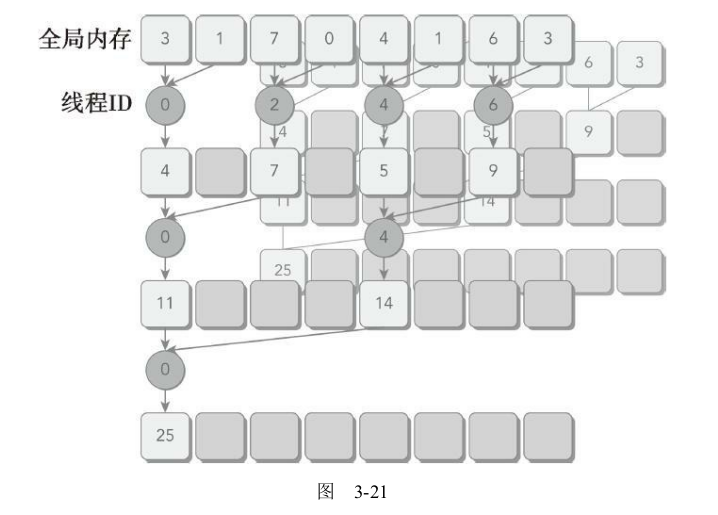
核函数代码如下
1 | // Neighbored Pair Implementation with divergence |
完整的执行逻辑如下
1 | // kernel 1: reduceNeighbored |
有几个点:
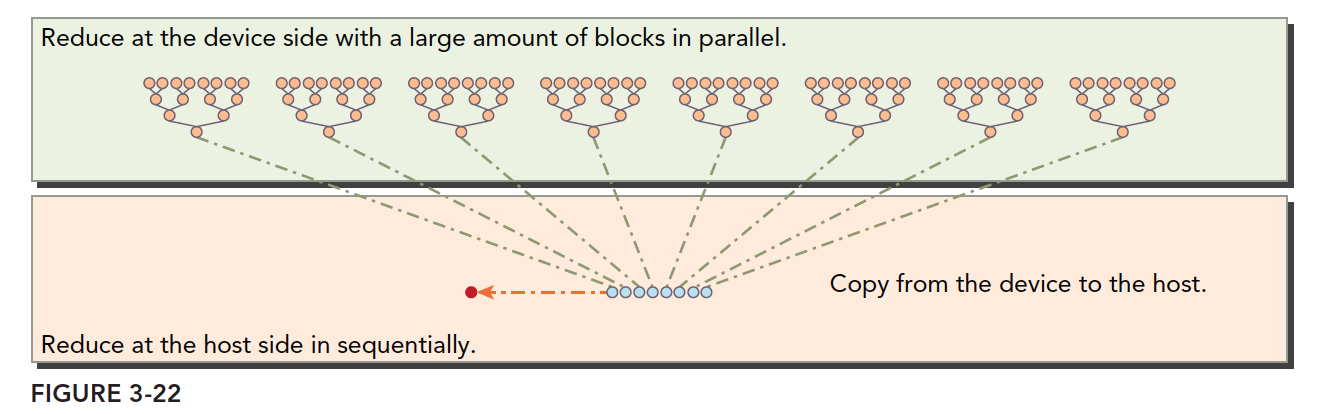
- 每个线程块处理数组的一部分,如图3-22中的一组橙色点,代表一个线程块的计算
- 线程块中每往下计算一行(一组橙色的点从一行运算到下一行)需要进行线程内同步,
__syncthreads();保障线程块内的其他线程运算完成。 - 所有线程块的计算结果在CPU中再进行求和,如图3-22中蓝色点。
3.4.3 改善并行归约的分化
上面的核函数有一个语句
1 | if ((tid % (2 * stride)) == 0) |
这句会导致线程分化。在并行归
约的第一次迭代中,只有ID为偶数的线程执行这个条件语句的主体,但是所有的线程都必须被调度。在第二次迭代中,只有四分之一的线程是活跃的,但是所有的线程仍然都必须被调度。
下面是一种解决方案,注意修改了线程的索引内存位置。
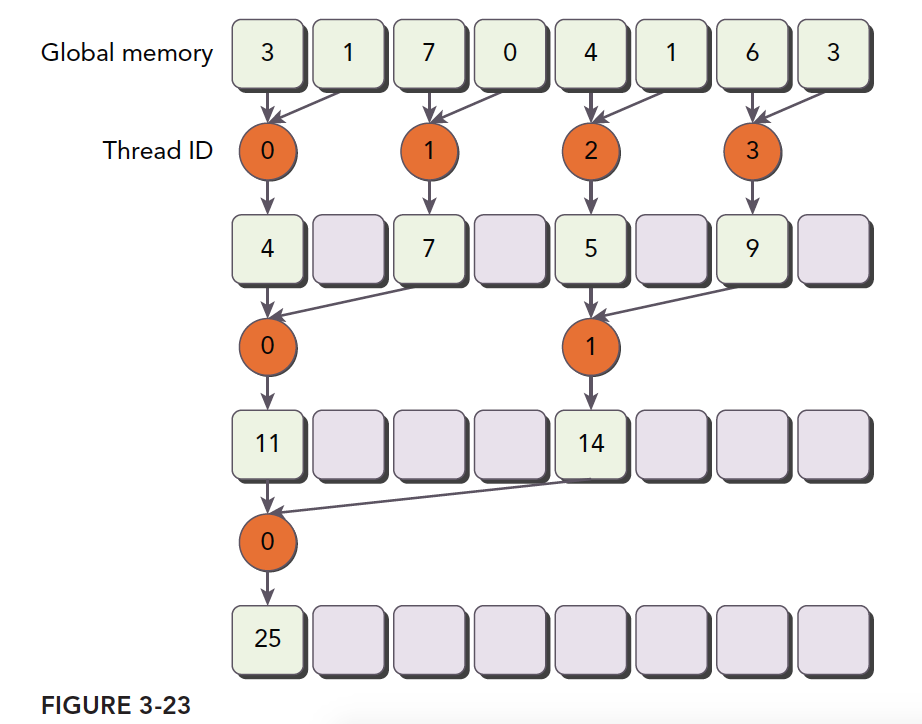
对应的核函数如下
1 | // Neighbored Pair Implementation with less divergence |
对于一个有512个线程的块来说,前8个线程束执行第一轮归约,剩下8个线程束什么也不做(虽然剩下的线程束没有做什么有用的工作,但是应该也会被调用运行啊,但是书中的意思是不运行,可能是内部的优化吧,不清楚为什么)。在第二轮里,前4个线程束执行归约,剩下12个线程束什么也不做。因此,这样就彻底不存在分化了。在最后五轮中,当每一轮的线程总数小于线程束的大小时,分化就会出现。在下一节将会介绍如何处理这一问题。
理解算法并不难,难在如何写成并行化的程序,其实需要注意几个点应该就可以写出来。
编写的
kernel函数实际上是一个block中运行的一部分线程,例如block(512,1,1),那么就是512个线程运行这一个kernel函数。当然会再细分为warp(32个线程一组)来执行单指令多线程SIMD。kernel函数实际上是对GPU内存的一些操作,因此需要确定的就是线程的索引和内存索引之间的对应关系。以
reduceNeighbored为例子说明1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11// in-place reduction in global memory
for (int stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride *= 2)//一个线程块内计算全部数组的一部分数据
{
if ((tid % (2 * stride)) == 0)//哪些线程是循环多次执行的
{
idata[tid] += idata[tid + stride];//线程操作的内存索引要计算正确
}
// synchronize within threadblock
__syncthreads();
}- 内存索引和线程索引是一致的。
- block(512,1,1),因此就是512个线程执行这一个
kernel函数,看似没有什么特别的,但是理解这一点很重要。有一些线程会循环多次执行(比如threadIdx.x=0),但是有些线程运行1次(比如threadIdx.x=2)。这就是为什么还会有一个for循环。 - 找出线程操作的内存和线程索引之间的关系,并计算。
3.4.4 交错配对的归约
与相邻配对方法相比,交错配对方法颠倒了元素的跨度。初始跨度是线程块大小的一半,然后在每次迭代中减少一半(如图3-24所示)。
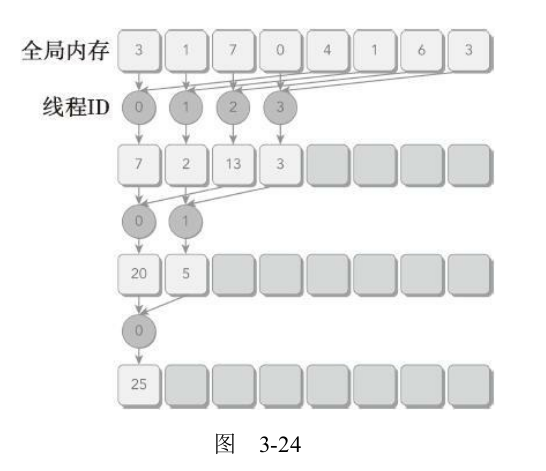
核函数代码如下
1 | // Interleaved Pair Implementation with less divergence |
使用nvprof分析如下
1 | sudo nvprof --metrics achieved_occupancy,inst_per_warp,gld_efficiency,gld_throughput ./reduceInteger |
1 | zmurder@zmurder:~/chapter03$ sudo nvprof --metrics achieved_occupancy,inst_per_warp,gld_efficiency,gld_throughput ./reduceInteger |
截图看的完整点
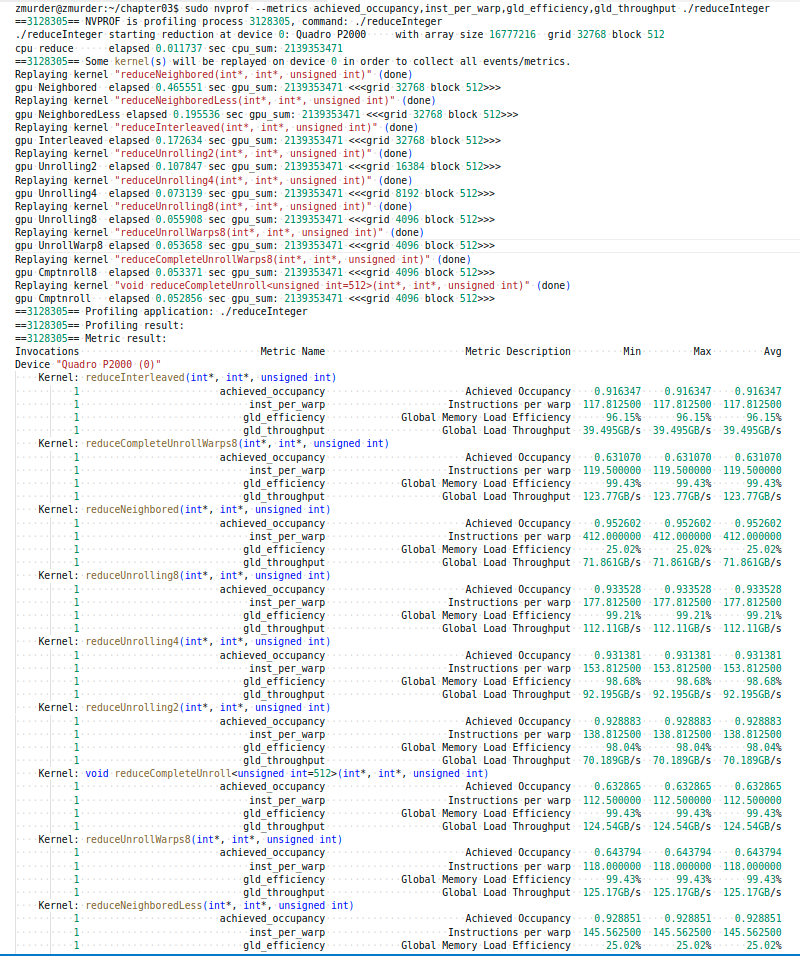
汇总表格如下
| gld_throughput | gld_efficiency | inst_per_warp | achieved_occupancy | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neighbored | 2.4549GB/s | 25.02% | 412.000000 | 0.952539 | 0.016720 sec |
| NeighboredLess | 4.9642GB/s | 25.02% | 145.562500 | 0.927764 | 0.010575 sec |
| Interleaved | 1.3862GB/s | 96.15% | 117.812500 | 0.916344 | 0.006903 sec |
其中achieved_occupancy应该是编译器优化了。