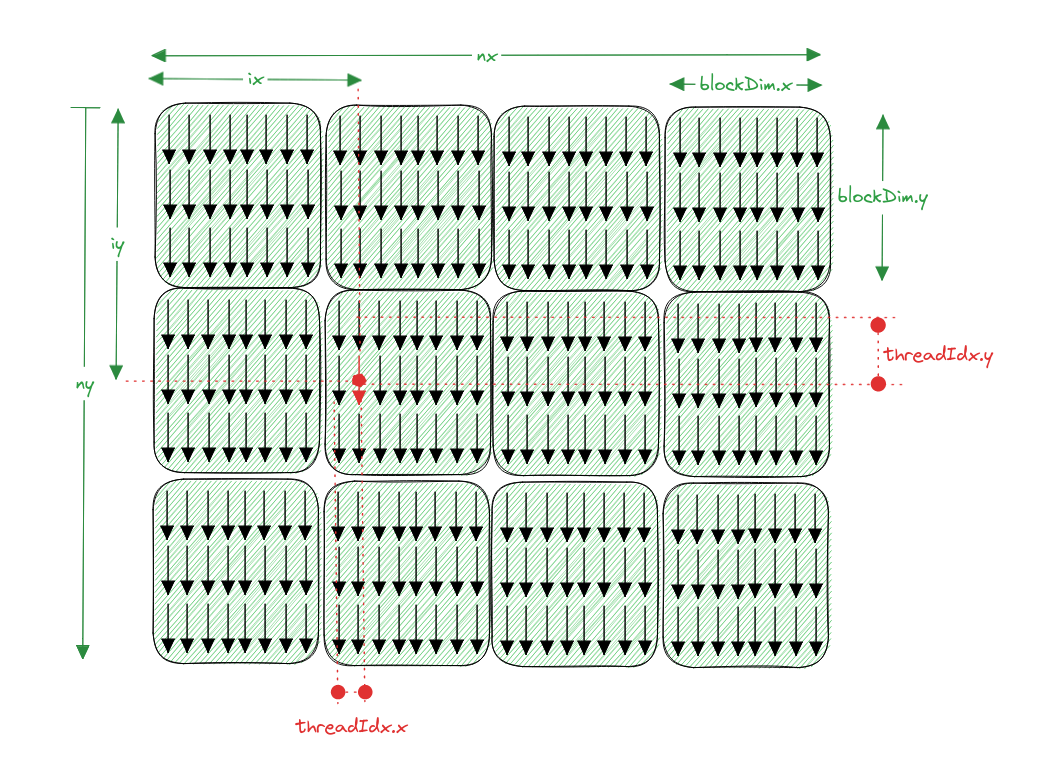
5.4 合并的全局内存访问 上一节介绍的是通过共享内存减少对全局内存的访问,这一部分是介绍使用共享内存避免对未合并的全局内存的访问。矩阵转置就是一个典型的例子:读操作被自然合并,但写操作是按照交叉访问的。在共享内存的帮助下,可以先在共享内存中进行转置操作,然后再对全局内存进行合并写操作。
5.4.1 基准转置内核 作为对比的基准,下面的核函数是一个仅使用全局内存的矩阵转置的实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 __global__ void naiveGmem (float *out, float *in, const int nx, const int ny) { unsigned int ix = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; unsigned int iy = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; if (ix < nx && iy < ny) { out[ix*ny+iy] = in[iy*nx+ix]; } }
下面图示可以更好的理解。
nvprof查看时间
1 2 3 4 5 Type Time (%) Time Calls Avg Min Max Name GPU activities: 54.09% 20.629ms 3 6.8764ms 6.8645ms 6.8945ms [CUDA memcpy DtoH] 20.30% 7.7420ms 1 7.7420ms 7.7420ms 7.7420ms [CUDA memcpy HtoD] 11.67% 4.4511ms 1 4.4511ms 4.4511ms 4.4511ms naiveGmem (float *, float *, int , int ) 3.55% 1.3557ms 1 1.3557ms 1.3557ms 1.3557ms copyGmem (float *, float *, int , int )
按照书中描述的,全局内存的读可能是32或者128字节的颗粒度,写是32字节的颗粒度。
加载和存储全局内存请求的平均事务的次数的测试结果如下(因为测试结果与书中差异太大了,因此再看看gld_efficiency和gst_efficiency 全局内存的加载和存储效率)。但是有一点是一致的,就是转置的存储内存请求事务数(gst_transactions_per_request)由拷贝的4变为了转置的32。明显的增多了,需要优化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 huolin@huolin:~/WorkSpace/zyd/note/cuda/CUDAC编程权威指南/CUDAC编程权威指南练习code/chapter05$ sudo nvprof --metrics gld_transactions_per_request,gst_transactions_per_request,gld_efficiency,gst_efficiency ./transposeRectangle ==127053== NVPROF is profiling process 127053, command: ./transposeRectangle ./transposeRectangle starting transpose at device 0: Quadro P2000 with matrix nrows 4096 ncols 4096 ==127053== Some kernel(s) will be replayed on device 0 in order to collect all events/metrics. Replaying kernel "copyGmem(float*, float*, int, int)" (done) copyGmem elapsed 0.135785 sec <<< grid (128,256) block (32,16)>>> effective bandwidth 0.988457 GB Replaying kernel "naiveGmem(float*, float*, int, int)" (done) naiveGmem elapsed 0.142126 sec <<< grid (128,256) block (32,16)>>> effective bandwidth 0.944357 GB ==127053== Profiling application: ./transposeRectangle ==127053== Profiling result: ==127053== Metric result: Invocations Metric Name Metric Description Min Max Avg Device "Quadro P2000 (0)" Kernel: copyGmem(float*, float*, int, int) 1 gld_transactions_per_request Global Load Transactions Per Request 16.000004 16.000004 16.000004 1 gst_transactions_per_request Global Store Transactions Per Request 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 1 gld_efficiency Global Memory Load Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 1 gst_efficiency Global Memory Store Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% Kernel: naiveGmem(float*, float*, int, int) 1 gld_transactions_per_request Global Load Transactions Per Request 16.000004 16.000004 16.000004 1 gst_transactions_per_request Global Store Transactions Per Request 32.000000 32.000000 32.000000 1 gld_efficiency Global Memory Load Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 1 gst_efficiency Global Memory Store Efficiency 12.50% 12.50% 12.50%
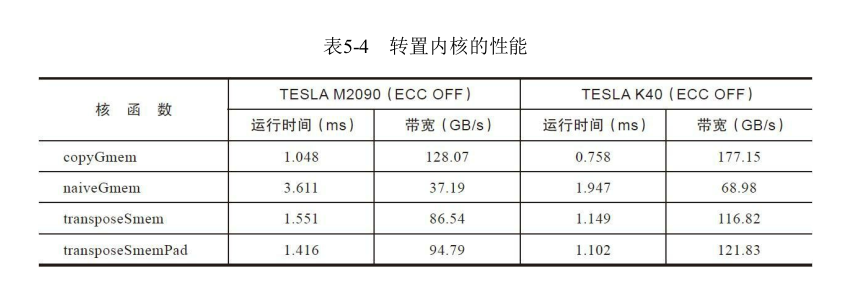
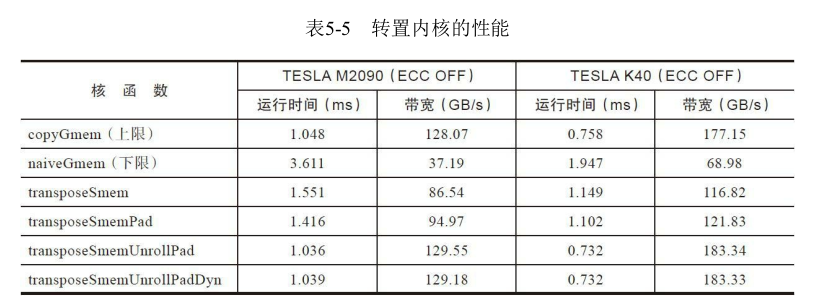
书中的测试结果如下
不知道为什么两个差异这么大。找资料没找到,先放一放吧。
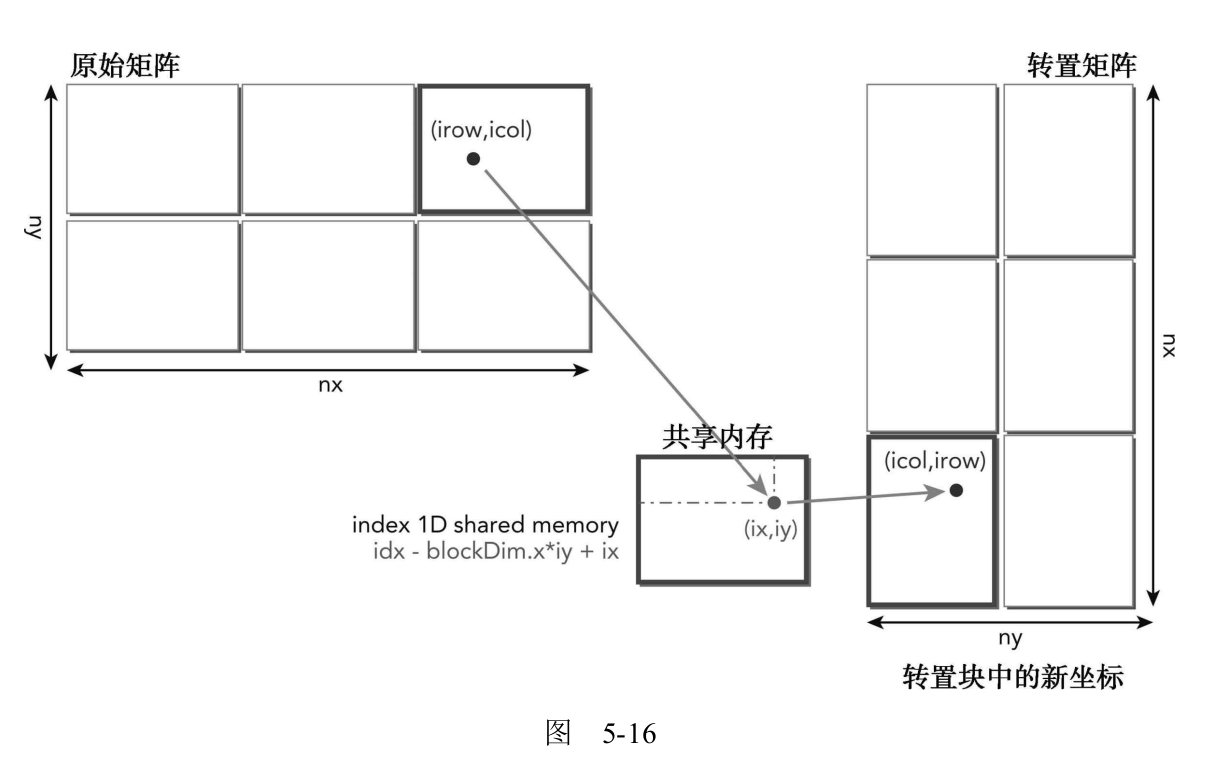
5.4.2 使用共享内存的矩阵转置 上一节的矩阵转置存储操作明显存在全局内存的交叉访问。为了避免交叉全局内存访问,可以使用二维共享内存来缓存原始矩阵的数据。从二维共享内存中读取的一列可以被转移到转置矩阵行中,它被存储在全局内存中。虽然下面的实现导致共享内存存储体冲突,但这个结果将比非合并的全局内存访问好得多。图5-15显
对应的核函数如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #define BDIMX 32 #define BDIMY 16 #define INDEX(ROW, COL, INNER) ((ROW) * (INNER) + (COL)) __global__ void transposeSmem (float *out, float *in, int nrows, int ncols) { __shared__ float tile[BDIMY][BDIMX]; unsigned int row = blockDim.y * blockIdx.y + threadIdx.y; unsigned int col = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; unsigned int offset = INDEX(row, col, ncols); if (row < nrows && col < ncols) { tile[threadIdx.y][threadIdx.x] = in[offset]; } unsigned int bidx, irow, icol; bidx = threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; irow = bidx / blockDim.y; icol = bidx % blockDim.y; col = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + icol; row = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + irow; unsigned int transposed_offset = INDEX(row, col, nrows); __syncthreads(); if (row < ncols && col < nrows) { out[transposed_offset] = tile[icol][irow]; } }
kerneltransposeSmem函数可被分解为以下几个步骤:
线程束执行合并读取一行,该行存储在全局内存中的原始矩阵块中。
该线程束按行主序将该数据写入共享内存中,因此,这个写操作没有存储体冲突。
因为线程块的读/写操作是同步的,所以会有一个填满全局内存数据的二维共享内存数组。
该线程束从二维共享内存数组中读取一列。由于共享内存没有被填充,所以会发生存储体冲突。
然后该线程束执行数据的合并写入操作,将其写入到全局内存的转置矩阵中的某行。
上面最难理解的就是各种索引的转换了。下图方便理解
nvprof查看时间
1 2 3 4 5 6 Type Time (%) Time Calls Avg Min Max Name GPU activities: 54.09% 20.629ms 3 6.8764ms 6.8645ms 6.8945ms [CUDA memcpy DtoH] 20.30% 7.7420ms 1 7.7420ms 7.7420ms 7.7420ms [CUDA memcpy HtoD] 11.67% 4.4511ms 1 4.4511ms 4.4511ms 4.4511ms naiveGmem (float *, float *, int , int ) 6.11% 2.3309ms 1 2.3309ms 2.3309ms 2.3309ms transposeSmem (float *, float *, int , int ) 3.55% 1.3557ms 1 1.3557ms 1.3557ms 1.3557ms copyGmem (float *, float *, int , int )
可以看出共享内存版本的比一般的转置快了一倍。
下面看看其他的数据,全局内存存贮和内存事务与拷贝已经一致了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 chapter05$ sudo nvprof --metrics gld_transactions_per_request,gst_transactions_per_request,gld_efficiency,gst_efficiency ./transposeRectangle [sudo] password for huolin: ==150723== NVPROF is profiling process 150723, command: ./transposeRectangle ./transposeRectangle starting transpose at device 0: Quadro P2000 with matrix nrows 4096 ncols 4096 ==150723== Some kernel(s) will be replayed on device 0 in order to collect all events/metrics. Replaying kernel "copyGmem(float*, float*, int, int)" (done) copyGmem elapsed 0.135283 sec <<< grid (128,256) block (32,16)>>> effective bandwidth 0.992126 GB Replaying kernel "naiveGmem(float*, float*, int, int)" (done) naiveGmem elapsed 0.149418 sec <<< grid (128,256) block (32,16)>>> effective bandwidth 0.898271 GB Replaying kernel "transposeSmem(float*, float*, int, int)" (done) transposeSmem elapsed 0.115023 sec <<< grid (128,256) block (32,16)>>> effective bandwidth 1.166876 GB ==150723== Profiling application: ./transposeRectangle ==150723== Profiling result: ==150723== Metric result: Invocations Metric Name Metric Description Min Max Avg Device "Quadro P2000 (0)" Kernel: copyGmem(float*, float*, int, int) 1 gld_transactions_per_request Global Load Transactions Per Request 16.000004 16.000004 16.000004 1 gst_transactions_per_request Global Store Transactions Per Request 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 1 gld_efficiency Global Memory Load Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 1 gst_efficiency Global Memory Store Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% Kernel: naiveGmem(float*, float*, int, int) 1 gld_transactions_per_request Global Load Transactions Per Request 16.000004 16.000004 16.000004 1 gst_transactions_per_request Global Store Transactions Per Request 32.000000 32.000000 32.000000 1 gld_efficiency Global Memory Load Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 1 gst_efficiency Global Memory Store Efficiency 12.50% 12.50% 12.50% Kernel: transposeSmem(float*, float*, int, int) 1 gld_transactions_per_request Global Load Transactions Per Request 16.000004 16.000004 16.000004 1 gst_transactions_per_request Global Store Transactions Per Request 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 1 gld_efficiency Global Memory Load Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 1 gst_efficiency Global Memory Store Efficiency 100.00% 100.00% 100.00%
5.4.3 使用填充共享内存的矩阵转置 为了消除共享内存的存储体冲突,添加列来操作。IPAD来指定填充的列数,需要根据不同的显卡来定,可以测试1或者2.看看效果。
1 __shared__ float tile[BDIMY][BDIMX + IPAD];
书中给出的结果如下
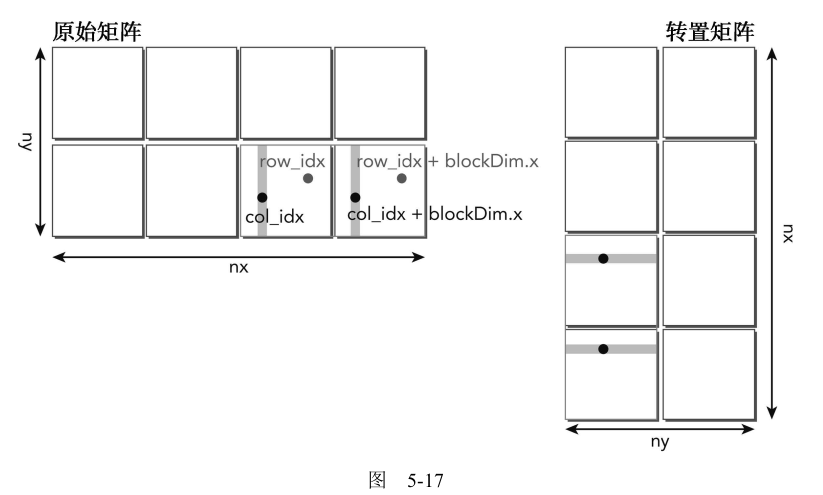
5.4.4 使用展开的矩阵转置 下面的核函数展开两个数据块的同时处理:每个线程现在转置了被一个数据块跨越的两个数据元素。这种转化的目标是通过创造更多的同时加载和存储以提高设备内存带宽利用率。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 __global__ void transposeSmemUnrollPad (float *out, float *in, const int nrows, const int ncols) { __shared__ float tile[BDIMY][BDIMX * 2 + IPAD]; unsigned int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; unsigned int col = (2 * blockIdx.x * blockDim.x) + threadIdx.x; unsigned int row2 = row; unsigned int col2 = col + blockDim.x; unsigned int offset = INDEX(row, col, ncols); unsigned int offset2 = INDEX(row2, col2, ncols); unsigned int bidx = threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; unsigned int irow = bidx / blockDim.y; unsigned int icol = bidx % blockDim.y; unsigned int transposed_offset = INDEX(col, row, nrows); unsigned int transposed_offset2 = INDEX(col2, row2, nrows); if (row < nrows && col < ncols) { tile[threadIdx.y][threadIdx.x] = in[offset]; } if (row2 < nrows && col2 < ncols) { tile[threadIdx.y][blockDim.x + threadIdx.x] = in[offset2]; } __syncthreads(); if (row < nrows && col < ncols) { out[transposed_offset] = tile[irow][icol]; } if (row2 < nrows && col2 < ncols) { out[transposed_offset2] = tile[irow][blockDim.x + icol]; } }
书中的测试结果如下
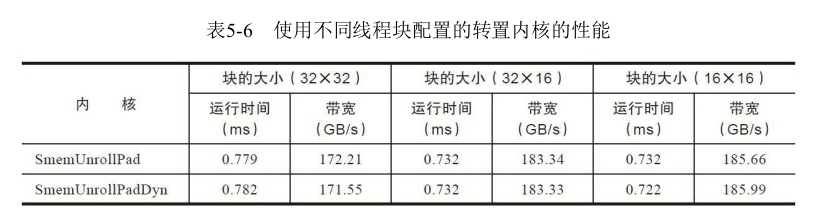
5.4.5 增大并行性 一个简单而有效的优化技术是调整线程块的维度,以找出最佳的执行配置。