1 简介 在深度学习中,为了提升数据传输带宽和计算性能,image 或 feature map在内存中的存放通常会使用NCHW、NHWC 和CHWN 等数据格式。例如常用的深度学习框架中默认使用NCHW的有caffe、NCNN、pytorch、mxnet等,默认使用NHWC的有tensorflow、openCV等
NCHW中,“N”batch批量大小,“C”channels特征图通道数,“H”特征图的高,和“W”特征图的宽。对于计算机而言,数据的存储只能是线性的
NCHW,又称:“channels_first”,是nvidia cudnn库原生支持的数据模式;在GPU中,使用NCHW格式计算卷积,比NHWC要快2.5倍左右(0:54 vs 2:14)
NHWC, 又称“channels_last”,是CPU指令比较适合的方式,SSE 或 AVX优化,沿着最后一维,即C维计算,会更快
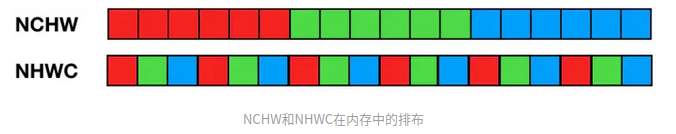
NCHW排列,C在外层,所以每个通道内,像素紧挨在一起,即“RRRGGGBBB”;NHWC排列,C在最内层,所以每个通道内,像素间隔挨在一起,即“RGBRGBRGB”,如下所示:
尽管存储的数据实际上是一样的,但是不同的顺序会导致数据的访问特性不一致,因此即使进行同样的运算,相应的计算性能也会不一样。对于”NCHW” 而言,其同一个通道的像素值连续排布,更适合那些需要对每个通道单独做运算的操作,比如”MaxPooling”。对于”NHWC”而言,其不同通道中的同一位置元素顺序存储,因此更适合那些需要对不同通道的同一像素做某种运算的操作,比如“Conv1x1”
由于NCHW,需要把所有通道的数据都读取到,才能运算,所以在计算时需要的存储更多。这个特性适合GPU运算,正好利用了GPU内存带宽较大并且并行性强的特点,其访存与计算的控制逻辑相对简单;而NHWC,每读取三个像素,都能获得一个彩色像素的值,即可对该彩色像素进行计算,这更适合多核CPU运算,CPU的内存带宽相对较小,每个像素计算的时延较低,临时空间也很小;若采取异步方式边读边算 来减小访存时间,计算控制会比较复杂,这也比较适合CPU。结论 :在训练模型时,使用GPU,适合NCHW格式;在CPU中做推理时,适合NHWC格式 。采用什么格式排列,由计算硬件的特点决定。OpenCV在设计时是在CPU上运算的,所以默认HWC格式。TensorFlow的默认格式是NHWC,也支持cuDNN的NCHW
2 python示例 下面的示例代码包含了两个操作,一个是BGR转RGB,另一个是HWC转CHW
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import cv2import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimg = cv2.imread("data/images/bus.jpg" ) img = cv2.resize(img, (5 ,4 )) print (img.shape) plt.figure() plt.imshow(img) plt.show() line1 = img[1 ,...] line1 = np.expand_dims(line1, axis=0 ) print (line1.shape)print (line1)plt.figure() plt.imshow(line1) plt.show() print ("BGR->RGB" )rgb_line1 = cv2.cvtColor(line1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) print (rgb_line1.shape)print (rgb_line1)print ()print ("HWC->CHW" )CHW_line1 = np.transpose(line1, (2 ,0 ,1 )) print (CHW_line1.shape)print (CHW_line1)
3 CUDA示例 一般情况下我们都使用opencv的imread()函数来读取图片,这里需要特别注意就读取彩色图像后得到的格式是BGR格式,像素值范围在0~255之间,通道格式为(H,W,C) 。如果需要使用GPU来处理,需要注意你自己的模型输入是BGR还是RGB,一般情况下我们的模型输入的都是NCHW格式(例如BBBGGGRRR这种排列),因此还需要转换
下面给出两个kernel,一个单独就是RGBA转BGR
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 __global__ void image_rgba_to_bgr_kernel (uint8_t *pImgIn, uint8_t *pImgOut, int w, int h, int bgr, int inputRgba) { int i, idx; uint8_t * dstPtr, * srcPtr; int id = (blockIdx.x + blockIdx.y*gridDim.x) * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; if (id >= w*h) return ; dstPtr = pImgOut+(id*3 ); if (1 == inputRgba) { srcPtr = pImgIn+(id*4 ); } else { srcPtr = pImgIn+(id*3 ); } for (i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { idx = i; if (bgr) { idx = (2 - i); } dstPtr[idx] = srcPtr[i]; } }
另一个示例应该是yolov5中的数据预处理中仿射变换示例代码,主要参考最后面的部分,包含了bgr to rgb 和HWC转CHW
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 __global__ void warpaffine_kernel ( uint8_t * src, int src_line_size, int src_width, int src_height, float * dst, int dst_width, int dst_height, uint8_t const_value_st, AffineMatrix d2s, int edge) { int position = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; if (position >= edge) return ; float m_x1 = d2s.value[0 ]; float m_y1 = d2s.value[1 ]; float m_z1 = d2s.value[2 ]; float m_x2 = d2s.value[3 ]; float m_y2 = d2s.value[4 ]; float m_z2 = d2s.value[5 ]; int dx = position % dst_width; int dy = position / dst_width; float src_x = m_x1 * dx + m_y1 * dy + m_z1 + 0.5f ; float src_y = m_x2 * dx + m_y2 * dy + m_z2 + 0.5f ; float c0, c1, c2; if (src_x <= -1 || src_x >= src_width || src_y <= -1 || src_y >= src_height) { c0 = const_value_st; c1 = const_value_st; c2 = const_value_st; } else { int y_low = floorf(src_y); int x_low = floorf(src_x); int y_high = y_low + 1 ; int x_high = x_low + 1 ; uint8_t const_value[] = {const_value_st, const_value_st, const_value_st}; float ly = src_y - y_low; float lx = src_x - x_low; float hy = 1 - ly; float hx = 1 - lx; float w1 = hy * hx, w2 = hy * lx, w3 = ly * hx, w4 = ly * lx; uint8_t * v1 = const_value; uint8_t * v2 = const_value; uint8_t * v3 = const_value; uint8_t * v4 = const_value; if (y_low >= 0 ) { if (x_low >= 0 ) v1 = src + y_low * src_line_size + x_low * 3 ; if (x_high < src_width) v2 = src + y_low * src_line_size + x_high * 3 ; } if (y_high < src_height) { if (x_low >= 0 ) v3 = src + y_high * src_line_size + x_low * 3 ; if (x_high < src_width) v4 = src + y_high * src_line_size + x_high * 3 ; } c0 = w1 * v1[0 ] + w2 * v2[0 ] + w3 * v3[0 ] + w4 * v4[0 ]; c1 = w1 * v1[1 ] + w2 * v2[1 ] + w3 * v3[1 ] + w4 * v4[1 ]; c2 = w1 * v1[2 ] + w2 * v2[2 ] + w3 * v3[2 ] + w4 * v4[2 ]; } float t = c2; c2 = c0; c0 = t; c0 = c0 / 255.0f ; c1 = c1 / 255.0f ; c2 = c2 / 255.0f ; int area = dst_width * dst_height; float * pdst_c0 = dst + dy * dst_width + dx; float * pdst_c1 = pdst_c0 + area; float * pdst_c2 = pdst_c1 + area; *pdst_c0 = c0; *pdst_c1 = c1; *pdst_c2 = c2; }
附录: 神经网络的数据排列:CHW与HWC
图像数据通道格式:NCHW和NHWC的区别
yolov5的TensorRT部署—warpaffine_cuda核函数
官方API解释:https://docs.opencv.org/3.4/db/d64/tutorial_js_colorspaces.html