Part4-TensorRT高级用法
1 背景
本文档是记录学习Nvidia官方B站的视频,参考对应的PDF文件 TensorRTTraining-TRT8.6.1-Part5-V1.1.pdf 的记录。对应的官方代码[trt-samples-for-hackathon-cn]
官方的视频教程基于TensorRT8.6.1版本。但是官方代码没有对应的tag。只有8.4、8.5和截至目前最新的8.10(master分支)。因此我这里参考的都是8.4分支的代码。
- part1 TensorRT简介
- part2 开发辅助工具
- part3 插件书写
- part4 TensorRT高级用法
- part5 常见优化策略
2 TensorRT高级用法
- 多 Optimization Profile
- 多 Context 与多 Stream
- CUDA Graph
- Timing Cache
- Algorithm Selector
- Refit
- Tactic Source
- Hardware compatibility 和 Version compatibility
- 更多工具
- 希望解决的问题
- Dynamic Shape 模式在 min-opt-max 跨度较大时性能下降?
- 怎样重叠计算和数据拷贝的时间,增加GPU利用率?
- 怎样使一个 engine 供多个线程使用?
- 怎么样优化 Kernel 的调用,减少 Launch Bound 的发生?
- engine 构建时间太长,怎么节约多次构建的时间?
- 某些 Layer 的算法导致较大的误差,能不能屏蔽掉该选择?
- 想更新模型的权重,但又不想重新构建 engine?
- 构建期/运行期显存占用过大,怎么减少?
- 能不能跨硬件或 TensorRT 版本运行 engine?
因为开发环境变化,这里使用的tensorrt都是TODO版本
2.1 多 OptimizationProfile
Dynamic Shape 模式在 min-opt-max 跨度较大时性能下降
解决方法:造多个 OptimizationProfile
范例代码08-Advance\MultiProfile
- 要点
- 缩小每个 Profile 范围,方便 TensorRT 自动优化,多个profile的动态范围可以重叠
- 推理时,根据数据形状选择相应 Profile
- 注意输入输出数据的绑定位置
- 间接作用
- 多 Context 的基础工作
- 增加显存占用、引擎尺寸和 .plan 尺寸
TODO 本机测试并验证,没看明白
1 | import numpy as np |
2.2 多stream
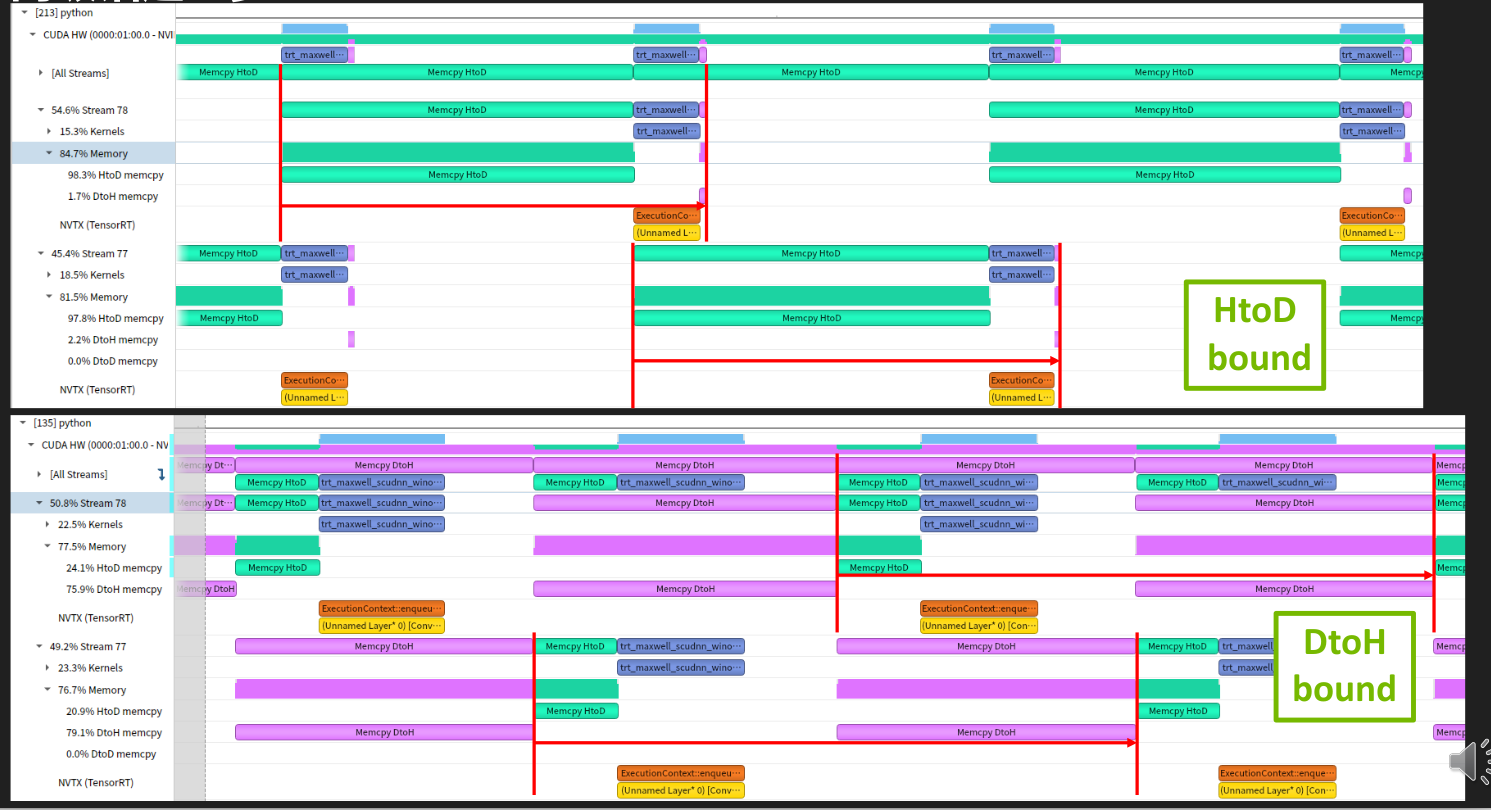
CUDA 编程经典话题:重叠计算和数据拷贝
- 解决方法:恰当使用 Stream
- 与GPU相关的异步操作,包括异步内存申请释放、kernel执行等,都可以放在一个或者多个stream中,同一个stream的函数调用会根据函数的加入顺序执行,不同的stream之间独立(不使用event时)
- 范例代码:08-Advance\MultiStream
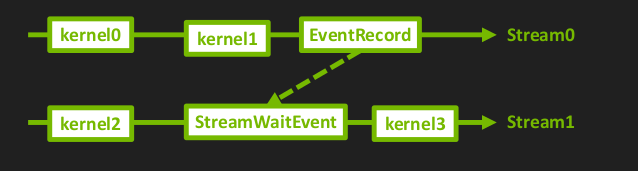
使用 CUDA event 和 CUDA stream
下图中stream0执行 kernel0-kernel1-eventRecord。同时stream2执行kernel2-StreamWaitEvent(等待stream0的eventRecord)-kernel3。
相当与kernel3必须在kernel0 1 2执行完成后再执行。
使用 pinned-memory
通常我们使用的CPU内存是可分页的,可以被交换到文件中以减少内存的使用量,但是pinned memory是不可分页的,一定在内存中。我们使用cuda的异步函数调用是一定要使用pinned memory。因为例如异步内存拷贝等都是异步的,真正执行的时候可能需要的内存被交换出去了,又要再换回来,浪费时间。
1 | import os |

2.3 多Context
一个 Engine 供多个 Context 共用,之占用一个engine的显存,供多个线程推理计算。
- 范例代码08-Advance\MultiContext
- 要点
- 从 engine 中创建多个 context
- contextList = [engine.create_execution_context() for index in range(nContext)
- 不再需要使用多个 OptimizationProfile (从TensorRT8.6开始),可以从示例代码中看细节
- 从 engine 中创建多个 context
1 |
|
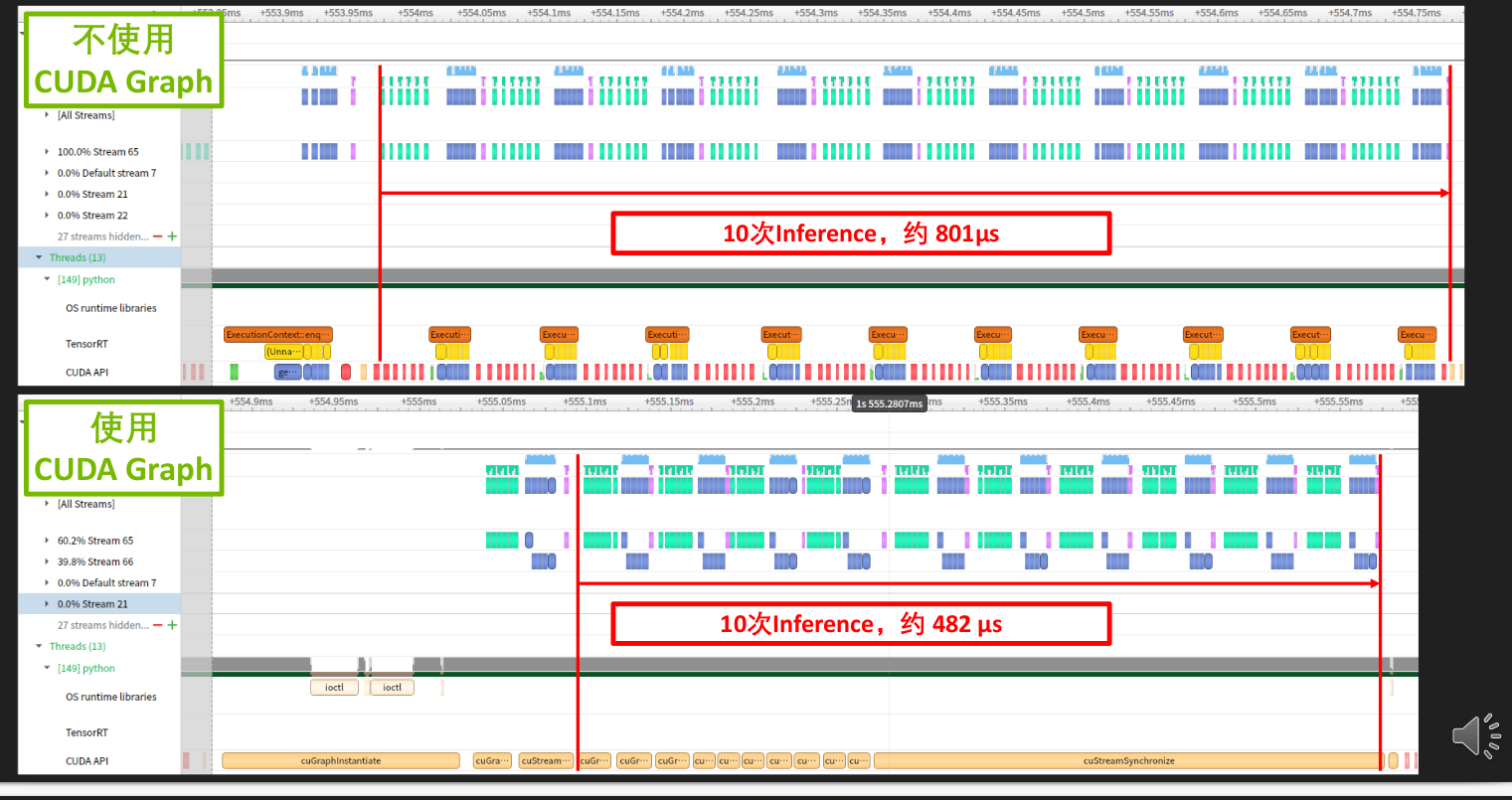
2.4 CUDA Graph
利用cuda Graph优化 Kernel 的调用,减少 Launch Bound 的发生
范例代码 08-Advance\CudaGraph
优点:
- 降低 CPU Launch cost
- CUDA 工作流优化
- 缓解大量 kernel 调用时的 Launch Bound
- 要点
- 步骤:Graph 定义, Graph 实例化, Graph 执行(捕获 CUDA Graph 之前要运行一次推理)
- Dynamic Shape 模式中,实际数据形状发生改变时(调用 context.set_binding_shape),
要先跑一遍 context.execute 再重新捕获 Graph,最后再实例化和执行 Graph
1 | /* |
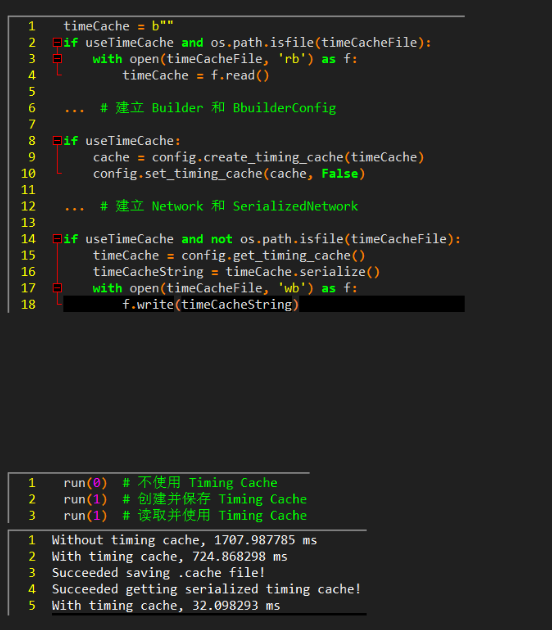
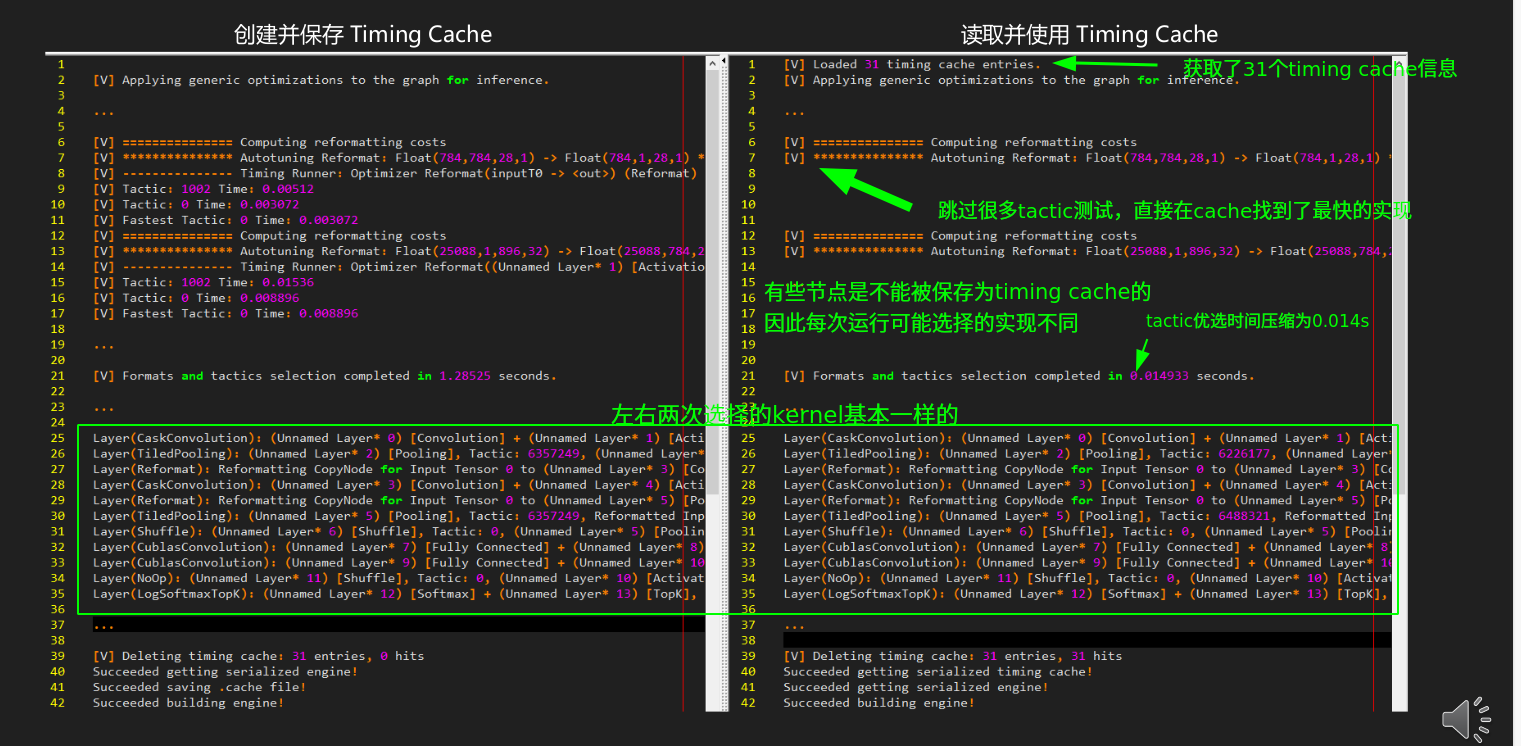
2.5 Timing Cache
engine 构建时间太长,使用timing cache节约多次构建时的时间
- 范例代码:08-Advance\TimingCache
- 优点:
- 优化单次引擎构建时间(模型内多个同参数的算子)
- 优化多次引擎构建时间(debug、参数更新后重新构建)
- 优化同环境下多个引擎构建时间(跨 builder 可用)
- 用于反复生成一模一样的引擎
- 要点
- 类似引擎序列化反序列化,将 Timing Cache 保存出来下次用
- 类似 .plan,不可跨平台和开发环境使用
1 | # |
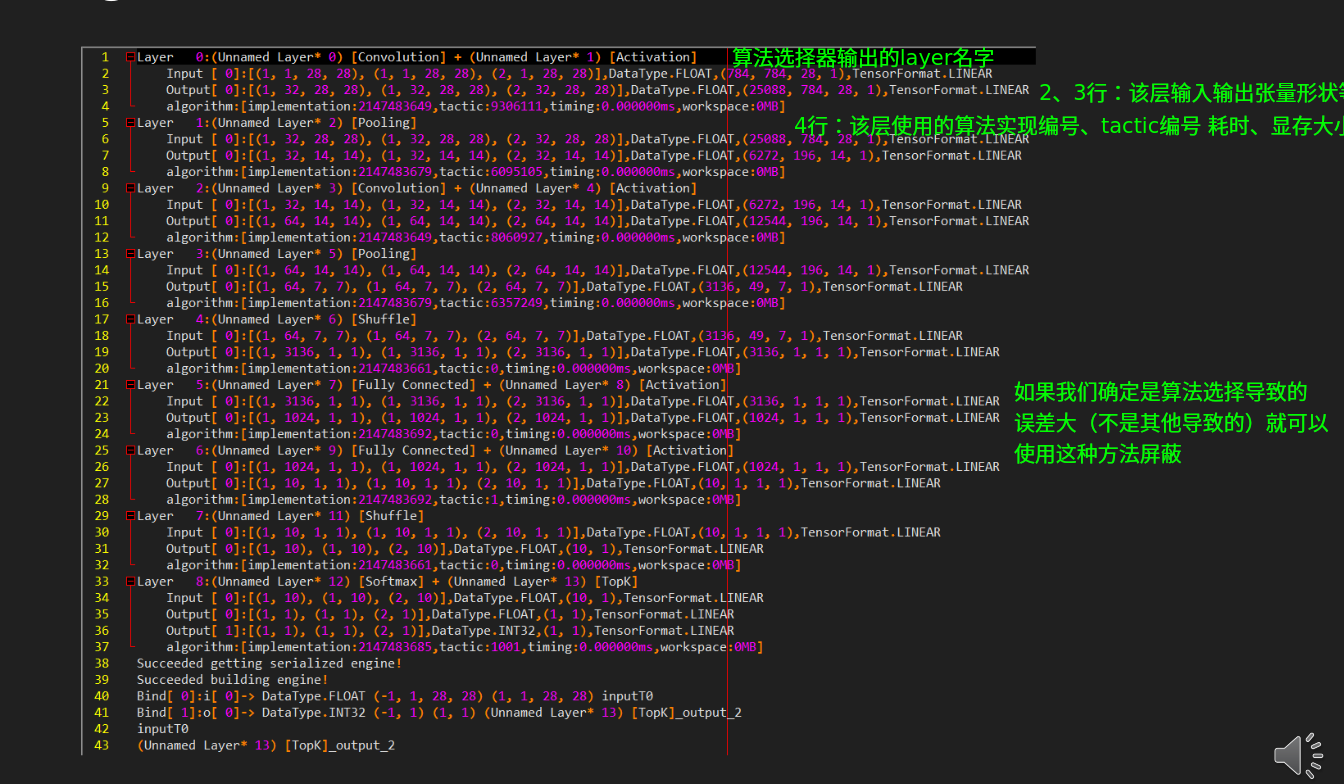
2.6 Algorithm Selector
TensorRT的kernel优选过程是一个黑箱,某些layer的选择可能造成较大的误差,我们需要筛选或排除某些算法。需要用到算法选择器。
- 样例代码08-Advance\AlgorithmSelector
- 要点
- 自己实现一个 MyAlgorithmSelector 类
- 关键是实现两个成员函数
- 一个用来挑选特定层的算法
- 一个用来报告所有层的挑选结果
- 构建网络时交给 BuilderConfig
- 实际工作流程:
- 先通过 polygraphy 等工具发现某层的个 Tactic 结果不理想
- 构造 Algorithm Selector 屏蔽掉盖层的该 tactic
- 构建引擎
1 | # |
代码中的algorithm.algorithm_variant.implementation == 2147483648这个数字就是手工挑选的算法,也可以使用不等号屏蔽算法。
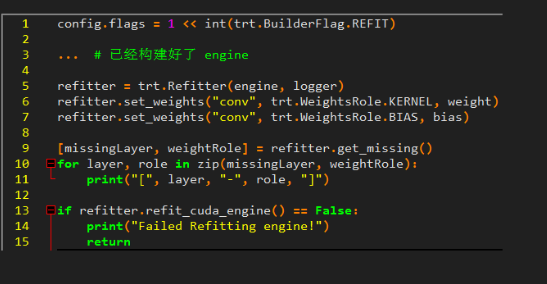
2.7 Refit
想更新模型的权重,但又不想重新构建 engine
适用与模型权重不停变化,的场景
优点
节约反复构建引擎的时间
强化学习必备
要点
- BuilderConfig 中设置相应 Flag
- 在构建好 engine 的基础上更新权重
- 更新某层权重后,邻近层可能也需要更新(尽管其值可能不变),如 Convolution 层中的 kernel 和 bias
[TensorRT] ERROR: 4: [refit.cpp::refitCudaEngine::1769] Error Code 4: Internal Error (missing 1 needed Weights. Call IRefitter::getMissing to get their layer names and roles or
IRefitter::getMissingWeights to get their weights names.) - 注意权重的排布方式
- Dynamic Shape 模式暂不支持(未来 TensorRT 版本将添加支持)
[TRT] [E] 4: [network.cpp::validate::2924] Error Code 4: Internal Error (Refittable networks with dynamic shapes is not supported.)
2.8 Tactic Source
- 要点
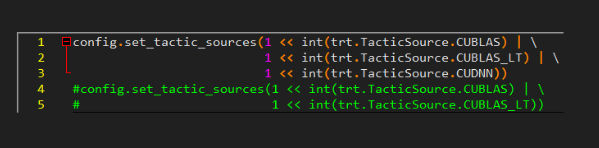
- BuilderConfig 中设置相应 Flag
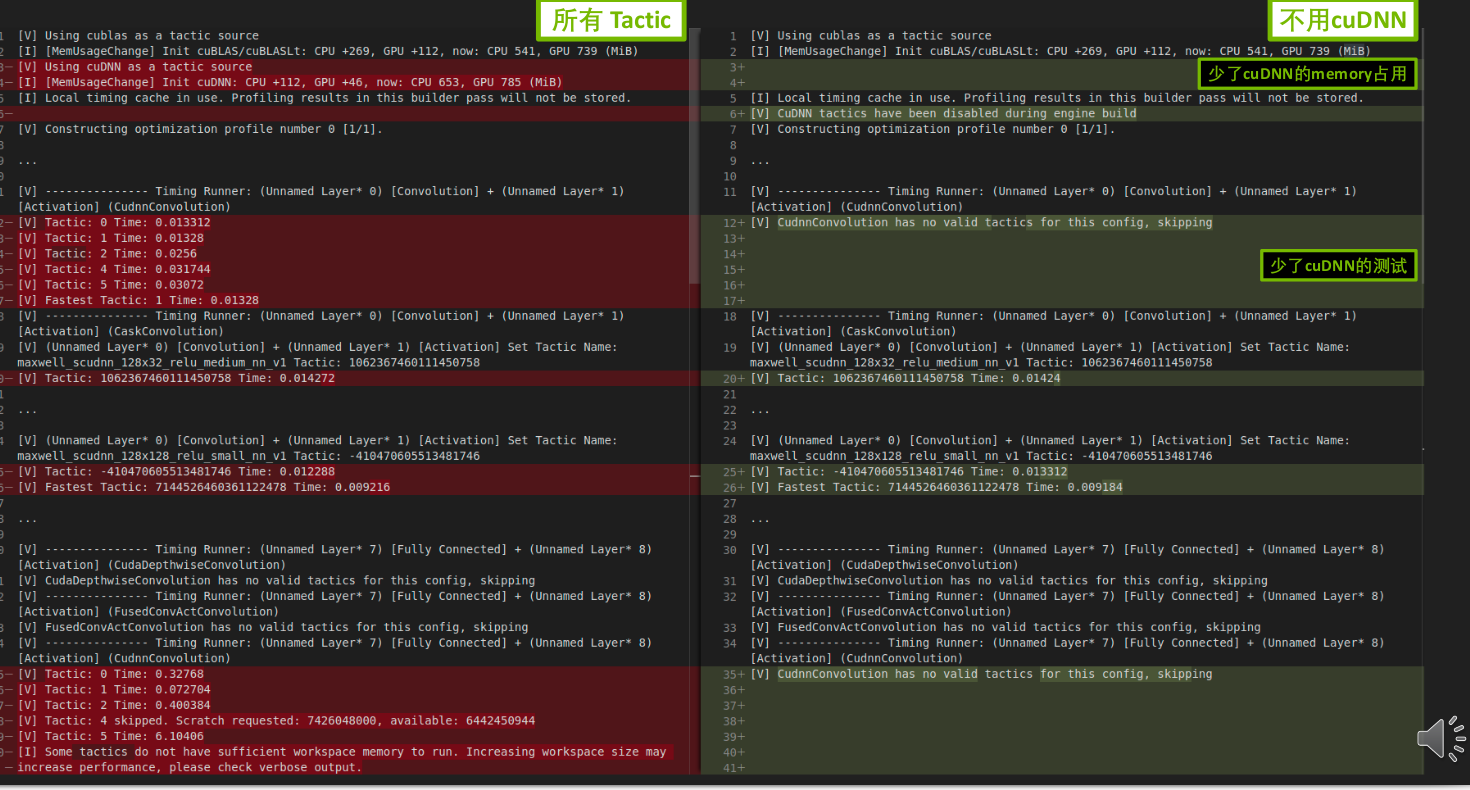
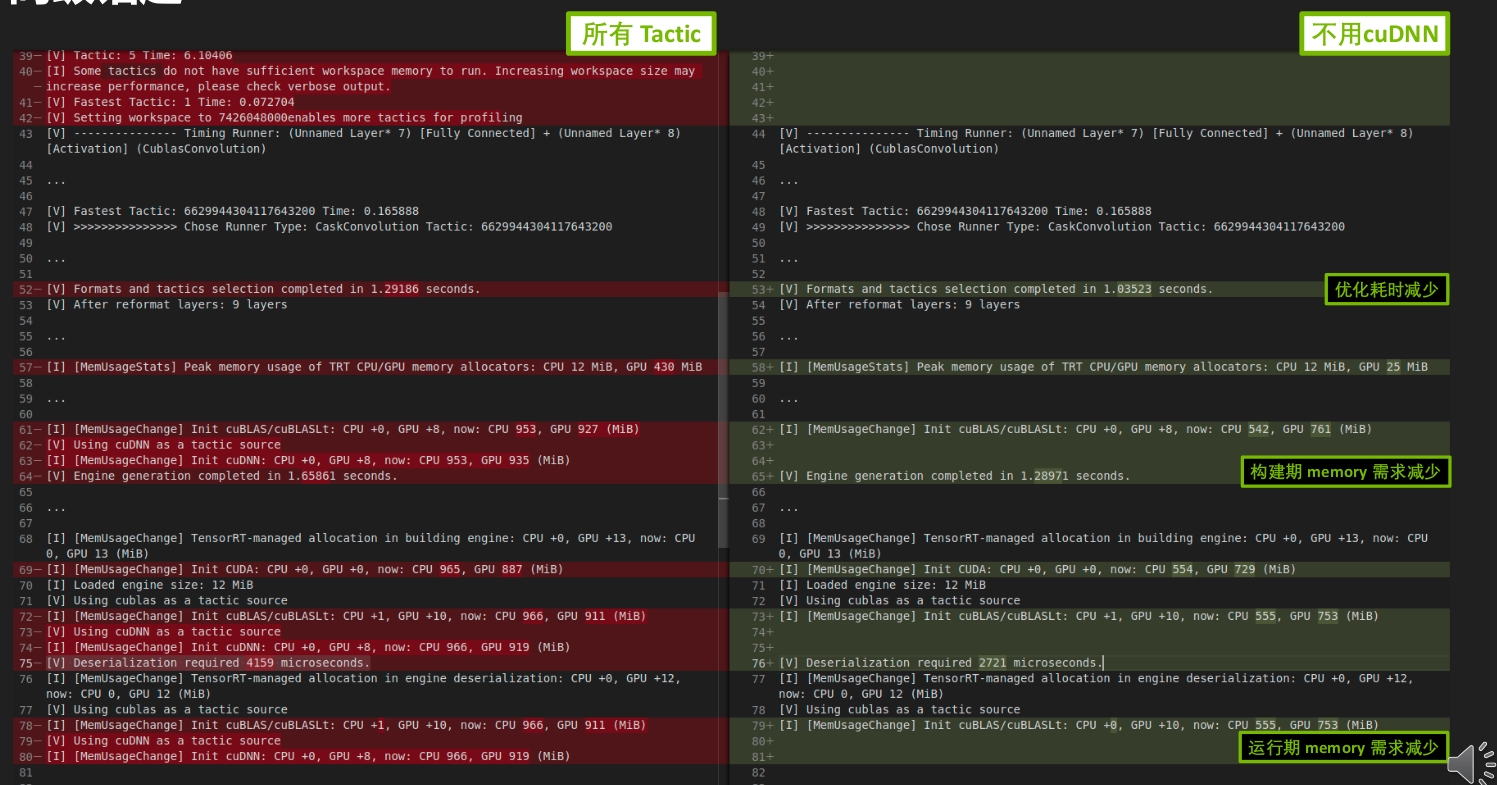
- 可以开启或关闭 cuBLAS、cuBLASLt、cuDNN(默认开启),tensorrt的tactic优选会从中找最优实现。
- 优点
- 节约部分内存、显存,减少构建时间
- 缺点
- 不能使用某些优化,可能导致性能下降
- 可能导致构建失败
- 后续版本中,TensorRT 将彻底断开对外部 Library 依赖
2.9 硬件兼容
TensorRT 8.6 新功能
- 硬件兼容只支持 Ampere 及更新架构的 GPU(sm ≥ 8.0),版本兼容要求 TensorRT 版本 ≥ 8.6
范例代码08-Advance/Hardware compatibility 和 08-Advance/ Version compatibility
硬件兼容
- config.hardware_compatibility_level = trt.HardwareCompatibilityLevel.AMPERE_PLUS
- 前向后向均可(A100 构建 A10 运行✔,A10 构建 A100 运行✔)
- 可能会有少许性能损失
版本兼容
- config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.VERSION_COMPATIBLE)
- runtime.engine_host_code_allowed = True
- 前向后向均可(TRT8.6 构
附录
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#cuda-graphs