Part5-3-TensorRT性能优化性能优化技巧
背景
本文档是记录学习Nvidia官方B站的视频,参考对应的PDF文件 TensorRTTraining-TRT8.6.1-Part5-V1.1.pdf 的记录。对应的官方代码[trt-samples-for-hackathon-cn]
官方的视频教程基于TensorRT8.6.1版本。但是官方代码没有对应的tag。只有8.4、8.5和截至目前最新的8.10(master分支)。因此我这里参考的都是8.4分支的代码。
- part1 TensorRT简介
- part2 开发辅助工具
- part3 插件书写
- part4 TensorRT高级用法
- part5 常见优化策略
这一部分为第五部分,对应上面的常见优化策略
性能优化技巧
General Tips
参考https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#optimize-performance
- Batching
- 增大batch size可以更好的发挥GPU算力,从而达到更高吞吐
- 如果吞吐随着batch size线性增加,一般说明GPU已打满
- Stream
- 单个execution context内多流并行:TRT 8.6提供了IBuilderConfig::setMaxAuxStreams() API 来设置steam数量
- 多个execution context间多流并行:设置不同stream
- 尽量避免使用default stream,否则会引入额外的implicit sync
- CUDA Graph
- 对于kernel launch bounded情况,可以通过CUDA graph来加速
- 不支持dynamic shape,需要capture多个CUDA Graph
- 设置nsys —cuda-graph-trace=node查看kernel
- Overhead of Shape Change and Optimization Profile Switching
- 当切换execution context或者改变graph input shape后,TRT可能会有额外的开销
- 可以尝试禁掉 kEDGE_MASK_CONVOLUTIONS tactic source,或者通过多个execution context切换使用来隐藏overhead
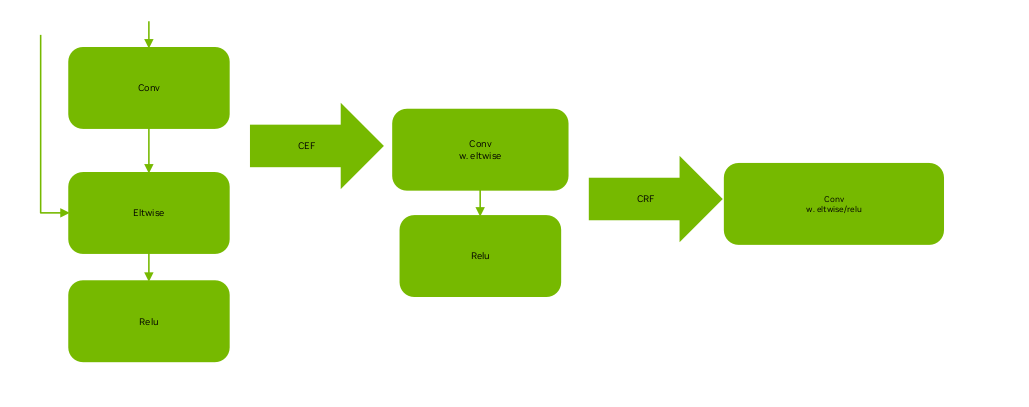
Graph Fusion 图融合
- Graph fusion是非常有效的手段,TRT内部支持了丰富的fusion pattern,比如经典的conv+bias+relu
- 如果你发现了通用而且有明显收益的pattern,但是TRT没有fuse,建议发个bug
- 我们可以通过onnx-graphsurgeon和TRT plugin来手动实现graph fusion,比如经典的LayerNorm plugin
- 我们可以利用TRT外部的资源,比如Cutlass,FlashAttn, xformer,将kernel implementation封装到TRT plugin
Optimizing Layer Performance Layer优化
参考链接:https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#optimize-layer
Reduce Layer
尽量保证reduce axis在最后一维,这样能保证数据连续性,从而实现更好的性能。手动加一写Transpose来保证。
如果reduce axis不在最后一维,可以通过Shuffle (transpose) 调整
解释:
Reduce Axis 在最后一维:如果
reduce axis设置为最后一维W,即dim=3,那么在内存中,数据是连续的。例如,对于一个形状为[1, 3, 224, 224]的张量,reduce axis=3的操作如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10import torch
# 创建一个 4D 张量
input_tensor = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
# 在最后一维上进行 reduce sum 操作
output_tensor = torch.sum(input_tensor, dim=3)
# 输出张量的形状为 [1, 3, 224]
print(output_tensor.shape)Reduce Axis 不在最后一维:如果
reduce axis设置为其他维度,例如C(即dim=1),那么在内存中,数据不是连续的。例如,对于一个形状为[1, 3, 224, 224]的张量,reduce axis=1的操作如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10import torch
# 创建一个 4D 张量
input_tensor = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
# 在第二维上进行 reduce sum 操作
output_tensor = torch.sum(input_tensor, dim=1)
# 输出张量的形状为 [1, 224, 224]
print(output_tensor.shape)
Shuffle Layer
- 如果input和output tensor有相同的memory layout,就不会有实际的kernel
MatMul Layer
如果使用FP16,而且K不是8的倍数,为了使用tensor core ,TRT可能会引入reformat kernel,可以通过手动padding到8的倍数来规避
如果input是4维,可以尝试通过reshape转化为3维或者2维,可能有更好的性能。不会有实际的keenle
解释:
在矩阵乘法(Matrix Multiplication)中,
M、N和K是三个重要的参数,它们分别表示输入矩阵的维度。具体来说,矩阵乘法的操作可以表示为:C=A×B
其中:
A是一个 M×K的矩阵。
B是一个 K×N的矩阵。
C是一个 M×N的矩阵。
Optimizing for Tensor Cores
参考链接:https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#optimize-tensor-cores
使用Tensor Core才能发挥GPU的最大算力,TF32,FP16,INT8,FP8
TRT的MatrixMultiply, FullyConnected, Convolution, and Deconvolution等计算密集的算子会使用Tensor Core
Tensor Core对data alignment有要求:

官网原文
1
2
3
4Tensor Core layers tend to achieve better performance if the I/O tensor dimensions are aligned to a certain minimum granularity:
The alignment requirement is on the I/O channel dimension in the Convolution and Deconvolution layers.
In MatrixMultiply and FullyConnected layers, the alignment requirement is on matrix dimensions K and N in a MatrixMultiply that is M x K times K x N.例如上面讲到的Matrix Multiplication中,
M、N和K。如果是TF32时K和N最好是4的倍数。对于卷积操作,假设输入特征图的形状为 (N,C,H,W),卷积核的形状为 (O,C,kH,kW),输出特征图的形状为 (N,O,oH,oW)。TF32:输入特征图的通道数 C必须是 4 的倍数。这里我不知道对于NHWC和NCHW都是对C的要求。
当tensor不满足alignment条件时,TRT会隐式地做padding,比如插入reformat layer
可以设置nsys —gpu-metrics-device all来查看Tensor Core使用情况
Tensor Layouts In Memory: NCHW vs NHWC
参考Tensor Layouts In Memory: NCHW vs NHWC
卷积通常对四维张量进行作: a batch composed of N “images” of C channels of H x W feature maps.
深度学习框架通常在内存中使用 NCHW 和 NHWC 布局(首字母缩略词列出了内存中从最慢到最快的维度)。布局选择会影响性能,因为为 Tensor Core 实现的卷积需要 NHWC 布局,并且在 NHWC 中布局输入张量时速度最快。
NCHW 布局仍然可以由 Tensor Core 进行作,但由于自动转置作而包含一些开销,如图 2 所示。当输入和输出张量较大或所需的计算量较低时(例如,当滤波器大小较小时),转置开销往往更显著。为了最大限度地提高性能,我们建议使用 NHWC 张量布局。
Figure 2. Kernels that do not require a transpose (NHWC) perform better than kernels that require one or more (NCHW). NVIDIA A100-SXM4-80GB, CUDA 11.2, cuDNN 8.1.
Channels In And Out
启用 Tensor Core 的要求取决于所使用的 cuDNN 版本。使用 cuDNN v7.6.3 及更高版本,卷积维度将在必要时自动填充以利用 Tensor Core。早期版本的 cuDNN 更严格:将 Tensor Core 与 NHWC 打包数据一起使用需要将 C 和 K 与 TF32 对齐为 4 的倍数,将 FP16 对齐为 8 的倍数,将 16 与 INT8 对齐为 16 的倍数。对于 NCHW 打包的 FP16 数据,通道将自动填充为 8 的倍数,以便启用 Tensor Core。但是,将 NCHW 数据与启用 Tensor Core 的内核一起使用会涉及一些额外的转置成本,这在内存中的 Tensor 布局:NCHW 与 NHWC 中进行了讨论。
另一方面,对于这些早期版本的 cuDNN,自动填充不会对 NHWC 打包的数据启动,因此会选择效率较低的回退内核,该内核不使用 Tensor Core 。鉴于 C 和 K 能被 8 整除,使用 NHWC 数据的卷积确实比使用 NCHW 数据的卷积表现更好。换句话说,如果某个图层已经与 NCHW 数据一起使用,则会发生自动填充;但是,如果正在使用 NHWC 数据,则选择或填充 C 和 K 为 8 的倍数可以提高性能。
对于 cuDNN v7.6.3 及更高版本,无论数据格式如何,填充都是自动的。填充会增加一些时间,尽管与启用 Tensor Core 的性能增益相比,这种成本通常可以忽略不计。值得注意的是,对于 FP16 选择 C 和 K 是 8 的倍数,或者对于其他数据类型选择等效值,效率最高:对于这些情况,不需要填充。
在某些情况下,通道数很小且不可协商。对于网络中的第一层,通常具有非常小的 C 值(灰度和 RGB 或 YCrCb 图像分别为 1 或 3)。特殊情况的卷积实现可以满足这一需求,特别是对于 C = 4 和 stride 为 2(图 8)。此处显示的数据是使用 cuDNN 8.1 收集的,因此填充是自动的。与 7.6.3 之前的版本相比,从 C = 3 到 C = 4 的性能改进没有那么剧烈,但选择 C = 4 仍然更快,因为不会发生填充。
图8.C = 4 的专用内核加快了卷积神经网络中的常见第一层(使用 NHWC 数据)的速度。选择 C = 4 或 8 的倍数可提供最佳性能。NVIDIA A100-SXM4-80GB、CUDA 11.2、cuDNN 8.1。
Low Precision 低精度
参考:https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring21-s31876/
- 使用低精度可以降低memory开销,其中FP16比较成熟,INT8需要PTQ或者QAT来保证精度,TRT接下来的版本会支持FP8
- INT8 QAT
- 量化感知训练(QAT)相比于训练后量化(PTQ)有更高的精度
- 训练阶段,TensorRT提供了基于PyTorch的INT8量化工具包,帮助生成QAT模型,并维持原有精
- 模型转换阶段, TensorRT ONNX parser新增了对ONNX QuantizeLinear和DequantizeLinear算子的支持推理阶段,TensorRT 8.0新增了Quantize
Sparsity 稀疏
参考
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring21-s31876/
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring21-s31552/
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/accelerating-inference-with-sparsity-using-ampere-and-tensorrt/
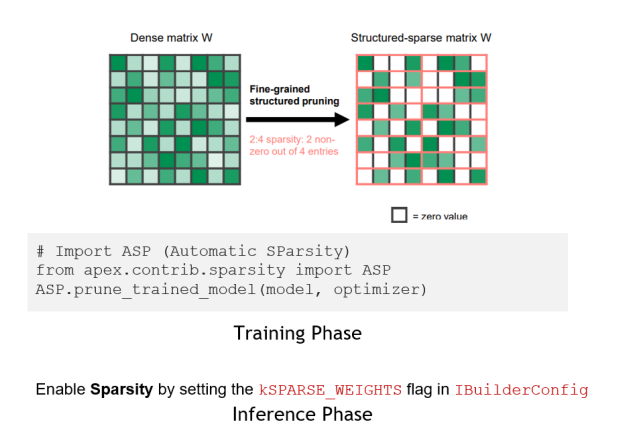
- TRT8.0支持了结构化稀疏,它是安培架构引入的新特性
- 利用结构化稀疏(structured sparsity)加速推理
- 通过2:4细粒度结构化稀疏减少一半参数,并利用SparseTensor Core进行加速,在Bert模型上能实现1.3倍的加速(下图针对w,4中个选最大的2个保留,剩下的作为一个mask,减少一半的参数量和一个mask)
- 训练阶段,通过稀疏化工具ASP (Automatic SParsity)修剪参数,然后微调模型以维持原有精度
- 推理阶段,通过设置build_config的SPARSE_WEIGHTS flag来挑选sparse kernel
- 可以通过trtexec —sparsity=enable/force来快速测试加速效果
Misc 其他
参考:https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#performance
- Optimizing Plugins 手动写plugin
- The performance of plugins depends on the CUDA code performing the plugin operation.
- Support as many formats as possible in the plugin. This removes the need for internal reformat operations during the execution of the network。自己写的plugin的不同的精度支持
- Optimizing Builder Performance 优化build engine的时间
- Timing cache
- Tactic Selection Heuristic
- Builder Optimization Level trt8.6引入的,设置不同的等级,例如更快设置为0 更好设置为5,正常是3
- Set the optimization
附录
- https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#optimize-performance
- https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#optimize-layer
- https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#optimize-tensor-cores
- https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring21-s31876/
- https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring21-s31876/
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring21-s31552/
https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/accelerating-inference-with-sparsity-using-ampere-and-tensorrt/ - https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html#performance
- fusion pattern
- Cutlass
- FlashAttn
- xformer